Mark-to-Market: A Deep Dive into This Accounting Method
It also ensures that the contract accurately reflects the price of the underlying asset. The trader then sets a stop loss at Rs. 45 to limit potential marked to market losses. This topic explains if an individual who buys and sells securities qualifies as a trader in securities for tax purposes and how traders must report the income and expenses resulting from the trading business. This topic also discusses the mark-to-market election under Internal Revenue Code section 475(f) for a trader in securities. Effective risk management is another crucial aspect facilitated by mark to market. By continuously updating asset values, financial institutions can identify and mitigate potential losses before they escalate.
How to Calculate the Ratio of a Selling Price to an Asking Price

One of the key applications of MTM accounting is in the valuation mark to market accounting of futures contracts. These contracts are agreements to buy or sell a specific asset at a future date at a predetermined price. Since the value of these contracts can change significantly over time, MTM accounting is used to adjust their value to reflect the current market price.
Problems with Historical Cost Accounting
The field of mark to market accounting is continuously evolving, driven by changes in regulations, market dynamics, and technological advancements. Staying ahead of these trends is essential for organizations to remain competitive and compliant. Mark to market accounting is now commonly used by many organizations to manage their credit risks. In this article, we will understand what the concept of mark to market is and how it helps in managing credit risks. This concept is crucial, adding layers of transparency to financial statements and reinforcing trust among https://healthnow.blog/accounting-equation-explained-formula-more/ investors.
Mark to Market and Financial Crises
This mechanism ensures that positions are properly collateralized, preventing a trader’s losses from affecting the broader market. Moreover, MTM ensures that financial statements represent the most current value of assets and liabilities. This up-to-date valuation allows stakeholders to make informed decisions based on the present market conditions, enhancing transparency and relevance in financial reporting.
Importance of Mark to Market in Financial Instruments
- To qualify as a trader, a person must be in the business of buying and selling securities with substantial, frequent, and continuous activity, with the intent to profit from short-term price swings.
- As a result, many businesses can go bankrupt, setting off a downward spiral that makes a recession worse.
- In contrast, mark to market accounting adjusts valuations based on current market prices, offering a dynamic and realistic view.
- When a bank issues loans, it creates an « allowance for credit losses » account that cushions against expected defaults.
- Similarly, a business that offers discounts to quickly fill up its accounts receivables (AR) will have to bring the AR to a lower value by using a contra asset account.
- The main downfall of the mark-to-marketing accounting principle is that the fair value upon which two sides have agreed may not reflect the actual worth of an asset.
- In this section, we will answer common questions about mark to market, its implications, and applications.
Mark to market (MTM) offers several advantages when it comes to financial reporting and investing, but it also comes with limitations and potential challenges. MTM provides a more up-to-date and transparent view of an institution’s or company’s assets, allowing stakeholders to understand the current value of these assets based on market conditions. For example, imagine an investor purchases 100 shares of a mutual fund priced at $25 per share on January 1st. At the end of each trading day, the NAV of the fund is calculated based on the current market value of its underlying investments. If the NAV increases to $26.25 by the end of the first day, the investor now has a total investment worth of $2,625 ($2,500 initial investment + $125 gain). Conversely, if the NAV decreases to $23.75, the investor’s total investment is now valued at $2,375 ($2,500 initial investment – $125 loss).

The mark-to-market accounting principle involves adjusting the value of an asset to reflect the current market conditions. In the Mental Health Billing closing month of the accounting year, each company must prepare financial statements where they report their asset value, among other things. The mark-to-market value for assets that are frequently traded is easy to determine. In such cases, the asset is valued at an amount the company would get if it sold the asset now.
The Impact of MTM on Major Financial Events
While MTM offers greater accuracy, it also introduces volatility into financial statements, especially during periods of market instability. MTM plays a critical role in futures and derivatives trading by requiring traders to adjust their positions daily based on current market prices. This daily marking ensures that gains and losses are accurately calculated and accounted for, helping traders maintain adequate margin levels and manage their risk effectively. The primary purpose of mark to market accounting is to provide an accurate and transparent representation of an organization’s financial position. By valuing assets and liabilities at their current market value, this approach ensures that financial statements reflect real-time economic conditions, aiding stakeholders in making informed decisions.

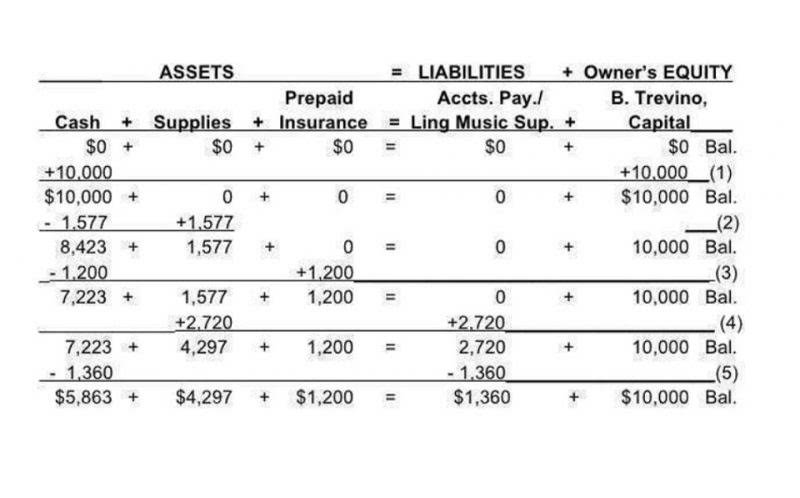
This can make it difficult for analysts to distinguish between core business activities and market-driven adjustments. Companies may need to provide additional disclosures to help users of financial statements understand the underlying drivers of reported results. The fundamental principles of Mark-to-Market (MTM) in accounting hinge on regular revaluation of assets and liabilities to reflect current market values.





